 https://www.mypinio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/How-to-find-promo-codes-easily.jpg
788
1400
mypinio
https://mypinio.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/mypinio_logo-1.png
mypinio2023-02-13 12:03:402023-02-13 12:06:15Promo Code: This is how easy you can find them to save money
https://www.mypinio.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/02/How-to-find-promo-codes-easily.jpg
788
1400
mypinio
https://mypinio.com/wp-content/uploads/2022/04/mypinio_logo-1.png
mypinio2023-02-13 12:03:402023-02-13 12:06:15Promo Code: This is how easy you can find them to save moneyWhat does semantic differential mean? A definition.
The semantic differential is a psychological measurement tool used to assess the meaning of words or concepts to people. It is based on the assumption that words or concepts do not have a single meaning, but rather that they consist of different components of meaning that can be arranged on a scale from positive to negative.
The semantic differential consists of a questionnaire containing a series of pairs of antipodes that have opposite meanings, for example “good” and “bad” or “old” and “young”. The respondent is asked to rate each pair on a scale of 1 to 7 or 1 to 5, where 1 represents the least extent of the term and 5 or 7 the most extent. The evaluation of the questionnaire makes it possible to quantify the importance of words or terms for the subjects and to make comparisons between different words or terms.
The semantic differential was developed by the psychologists Charles Osgood, George J. Suci and Percy H. Tannenbaum. It is often used in market research and advertising to gauge people’s reactions to certain products or services. It is also used in psychology to study the meaning of words or concepts to people and to analyse people’s personality traits.
Example of a semantic differential
In the following example of a semantic differential, the respondent would place a mark on the scale that she thinks best describes how she feels about the word “family” in relation to the qualities listed. For example, if she perceives the word “family” to be very happy, loving and stable, she would possibly position herself near the “Happy”, “Loving” and “Stable” pole. If, on the other hand, she perceives the word “family” as unhappy, unloving and unstable, she would possibly position herself near the pole “Unhappy”, “Unloving” and “Unstable”.
| 2 | 1 | 0 | -1 | -2 | ||
| happy | x | unhappy | ||||
| lovingly | x | unlovingly | ||||
| stable | x | unstable | ||||
| satisfied | x | unsatisfied |
The semantic differential is evaluated by calculating averages for the two adjectives in each pair of scales and then presenting the results in the form of charts or graphs. The results can then be used to understand and analyse people’s attitudes and opinions about specific topics or objects.
How to calculate the result of a semantic differential?
There is no standard formula to calculate the semantic differential as it depends on the specific study and the dimensions used. However, it is common to record the subjects’ ratings on a scale of, for example, -100 to 100 or -7 to 7 and then subtract the negative ratings from the positive ratings to calculate the semantic differential.
Another option is to use correlations to calculate the associations of the words or phrases with different dimensions. In any case, it is important that the dimensions used are clearly defined and that all subjects use the same scale to give their assessments in order to obtain valid results.
In der Regel stellt man die Ergebnisse des semantischen Differenzials mit einem bipolaren Diagramm dar. Für das Beispiel oben sähe das wie folgt aus:
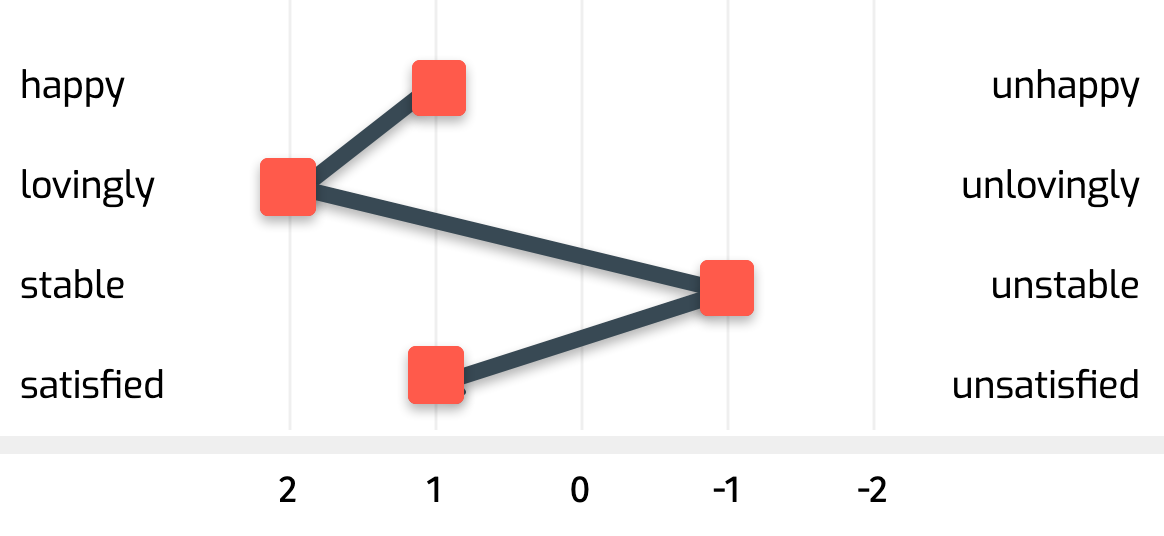
Excursus: What is a bipolar diagram?
Ein bipolares Diagramm, auch als bipolares Koordinatensystem oder Doppelskalendiagramm bezeichnet, ist eine Art von Diagramm, das zwei unterschiedliche Skalen verwendet, um Daten darzustellen. Eine Skala wird normalerweise für positive Werte verwendet und die andere Skala für negative Werte. Es werden normalerweise zwei parallele Achsen verwendet, von denen eine die positive und die andere die negative Skala darstellt. Jeder Punkt im Diagramm wird durch die Koordinaten auf den beiden Skalen beschrieben, die die Position des Punkts im Diagramm bestimmen. Bipolare Diagramme werden häufig verwendet, um Daten darzustellen, die sowohl positive als auch negative Werte haben und die Beziehungen zwischen den beiden Arten von Werten hervorheben.
Further ways of analysing semantic differentials
Wenn du mehrere Antworten von Probanden miteinander vergleichen möchtest, dann kannst du dieses ganz einfach tun, indem du die Ergebnisse jeden einzelnen Probanden in unterschiedlichen Farben darstellst.
Unübersichtlich wird dies jedoch, wenn du eine große Anzahl von Probanden hast. Hier ermittelt man das Ergebnis des semantischen Potenzials anhand von Durchschnittswerten und stellt dies ebenso in Form des oben gezeigten Diagramms dar.
Um den Durchschnittswert für die Darstellung des semantischen Differenzials in einem bipolaren Diagramm zu berechnen, musst du zunächst, bezogen auf das obige Beispiel, die Daten für alle 100 Probanden und alle 5 Ausprägungen sammeln. Dann musst du für jede Ausprägung die Bewertungen aller Probanden zusammenfassen und durch die Anzahl der Probanden teilen, um den Mittelwert für jede Ausprägung zu erhalten.
Das semantische Differenzial läßt sich auch anhand der Häufigkeitsverteilung in einer Tabelle darstellen, wie im folgenden Beispiel.
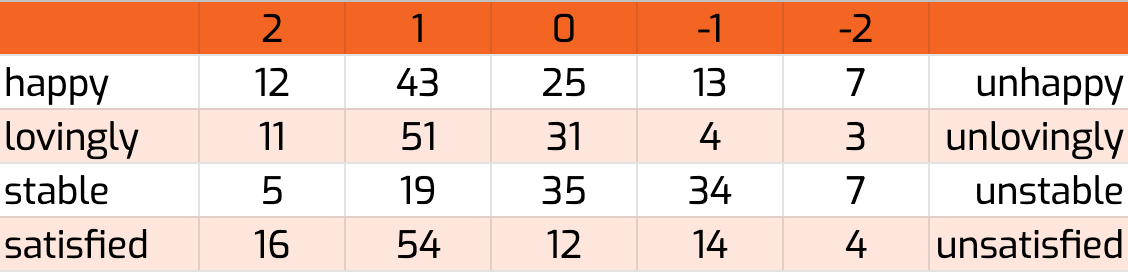
Die erste Spalte zeigt, dass 44 Teilnehmer eine Bewertung von -2 gegeben haben. Diese Bewertungen sind in den anderen Spalten auf die einzelnen Attribute und deren Gegenstücke aufgeteilt. Zum Beispiel haben 12 Teilnehmer eine Bewertung von -2 für das Attribut “happy” gegeben und 7 Teilnehmer haben eine Bewertung von -2 für das Attribut “unhappy” gegeben.
Aus diesen Daten könnte man eine Unmenge an Informationen herausziehen und diese grafisch darstellen, etwa im folgenden Diagramm:
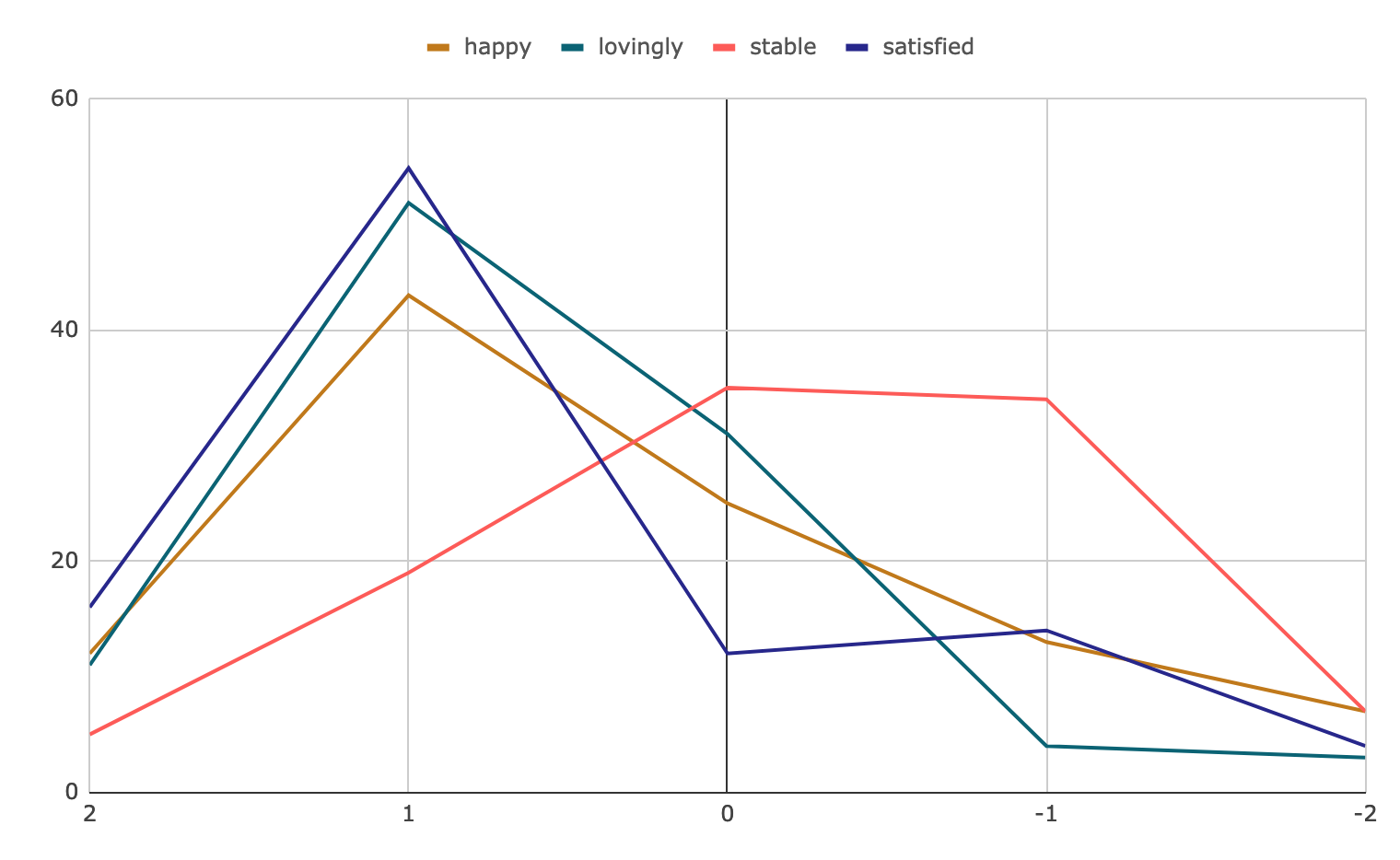
Es ist möglich, die Ergebnisse weiter zu analysieren, um Muster und Trends in den Antworten der Teilnehmer zu erkennen. Zum Beispiel kann man sehen, dass eine höhere Anzahl von Teilnehmern eine positive Bewertung für das Attribut “lovingly” gegeben haben im Vergleich zu “unlovingly”.
What are the advantages of the semantic differential?
An important advantage of the semantic differential is that it allows for a quantitative measurement of attitudes and attributes. By using scales that indicate how positively or negatively a term is evaluated by a person, we can make direct comparisons between different terms or concepts.
Another advantage of the semantic differential is that it is a relatively simple and quick method to capture attitudes and attributes. It is also very flexible and can be used in many different contexts, including market research, advertising research and political opinion research.
Finally, the semantic differential is a useful method to capture the subjective meaning of terms and concepts. It can help to understand people’s attitudes and attributes in ways that might be difficult to capture if relying on direct questions or other methods.
What are the disadvantages of semantic differential?
One disadvantage of the semantic differential is that it only measures subjective opinions and impressions, which can vary from person to person. There are no objective criteria against which the results can be judged. Therefore, the results of the semantic differential can easily be influenced by individual prejudices, expectations and personal experiences.
Another disadvantage is that the semantic differential can only map a limited number of properties, which are stated in terms of antipodes (two opposite adjectives). This means that it may not be able to fully map the complex and multi-layered meaning of concepts or objects.
Finally, the semantic differential may also tend to elicit unintended or unintentional responses from participants who consciously or unconsciously deviate from the norm. This can affect the accuracy and reliability of the results.
read also
#marketresearch #maxdiff #netpromoterscore #likertscale #insightscommunity
[shariff]
Keywords of this blog post
semantic differential | example | definition




